Day 44: Simple Linear Regression Theory
The Foundation of Predictive AI
What We’ll Build Today
Understand the mathematical foundation of linear regression from first principles
Implement simple linear regression from scratch (no scikit-learn yet)
Learn how gradient descent finds optimal prediction lines
Connect regression theory to production AI systems at Netflix, Zillow, and Tesla
Why This Matters: The Algorithm Behind Billions of Predictions
Every time Netflix predicts you’ll rate a movie 4.2 stars, Zillow estimates a house price, or Tesla’s autopilot calculates braking distance, linear regression is working behind the scenes. It’s the most widely deployed supervised learning algorithm in production AI systems.
Real-world impact: Google’s ad bidding system processes millions of linear regression predictions per second to estimate click-through rates. Understanding how this algorithm works from first principles gives you the foundation for neural networks, gradient boosting, and every advanced ML technique you’ll learn.
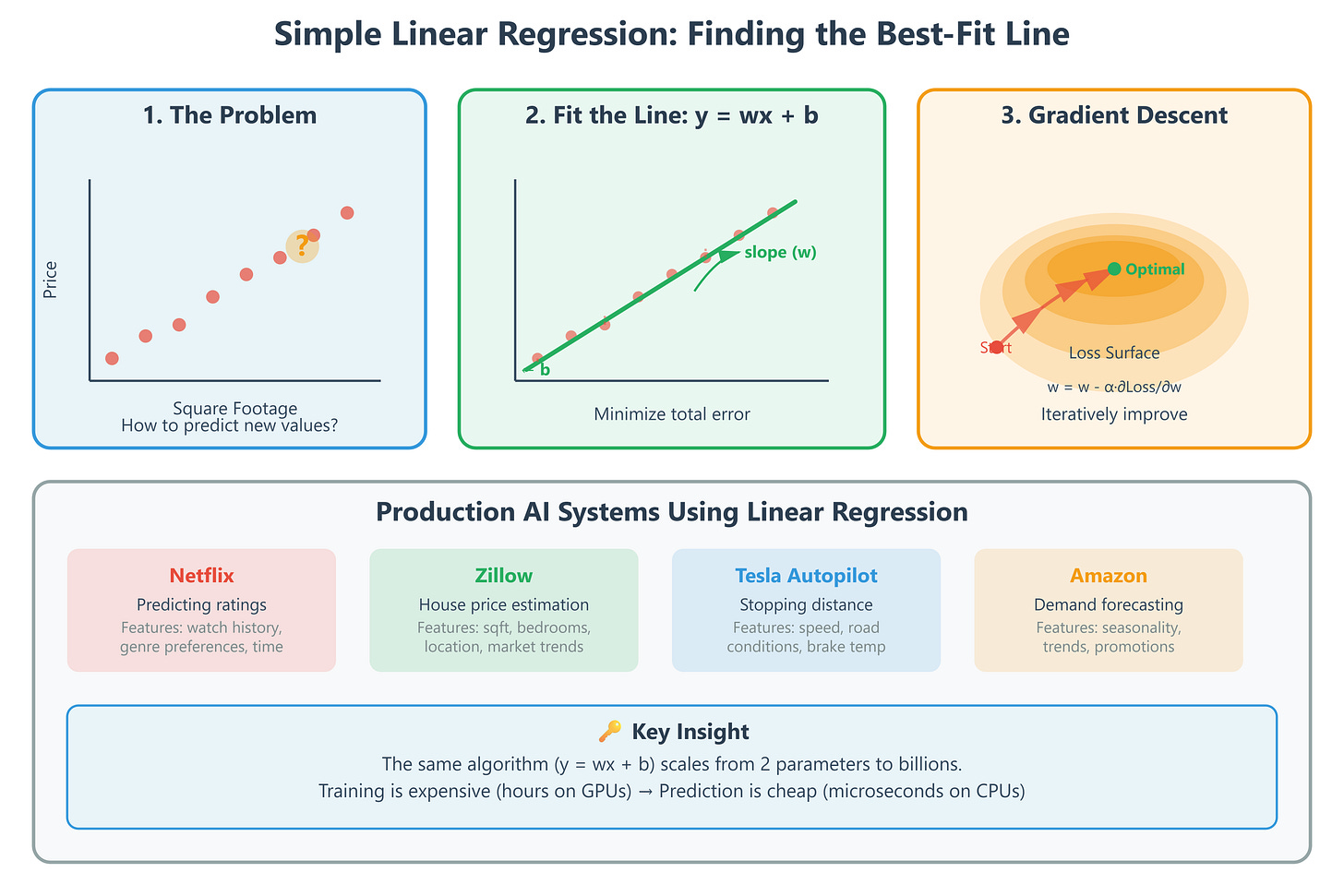
Here’s what makes linear regression powerful: it finds the optimal straight line through your data by mathematically minimizing prediction errors. The same core algorithm that predicts house prices with 10 data points scales to Netflix’s system predicting ratings across 200 million users.
Core Concept: Finding the Best-Fit Line Through Mathematics
The Problem: From Points to Predictions
Imagine you’re building Zillow’s house price predictor. You have data: 1200 sq ft → $250k, 1800 sq ft → $320k, 2400 sq ft → $410k. How do you predict the price of a 2000 sq ft house you’ve never seen?
Linear regression says: “Find the straight line that best fits these points, then use that line for predictions.” The line equation is simple: y = mx + b (or in ML notation: ŷ = wx + b).
w (weight/slope): How much price changes per square foot
b (bias/intercept): Base price when size is zero
x (feature): Square footage
ŷ (prediction): Estimated price
The critical insight: We don’t guess these values. We calculate them mathematically by minimizing the total error across all training examples.