Day 42: Data Splitting (Train/Test/Validation)
Module 1: Foundational Skills | Week 7: Core Concepts | Day 42 of 180
What We’ll Build Today
Split datasets into train/test/validation sets using scikit-learn
Implement stratified splitting for imbalanced datasets
Build a production-grade data pipeline with proper splitting logic
Understand why Netflix tests recommendations on 10% of users before full rollout
Why This Matters: The $100M Mistake You Can Avoid
Remember Day 41 when we learned about overfitting? Here’s the brutal reality: your model might show 99% accuracy on training data but completely fail in production. This happens at scale every day.
Netflix doesn’t test new recommendation algorithms on all 230 million subscribers simultaneously. Tesla doesn’t deploy Autopilot updates to every vehicle at once. Google doesn’t roll out search ranking changes to all users immediately. Why? Because testing on the same data you trained on is like practicing a test with the answer key, then being surprised when the real exam is different.
Data splitting is how production AI systems prevent catastrophic failures. It’s your insurance policy against deploying broken models.
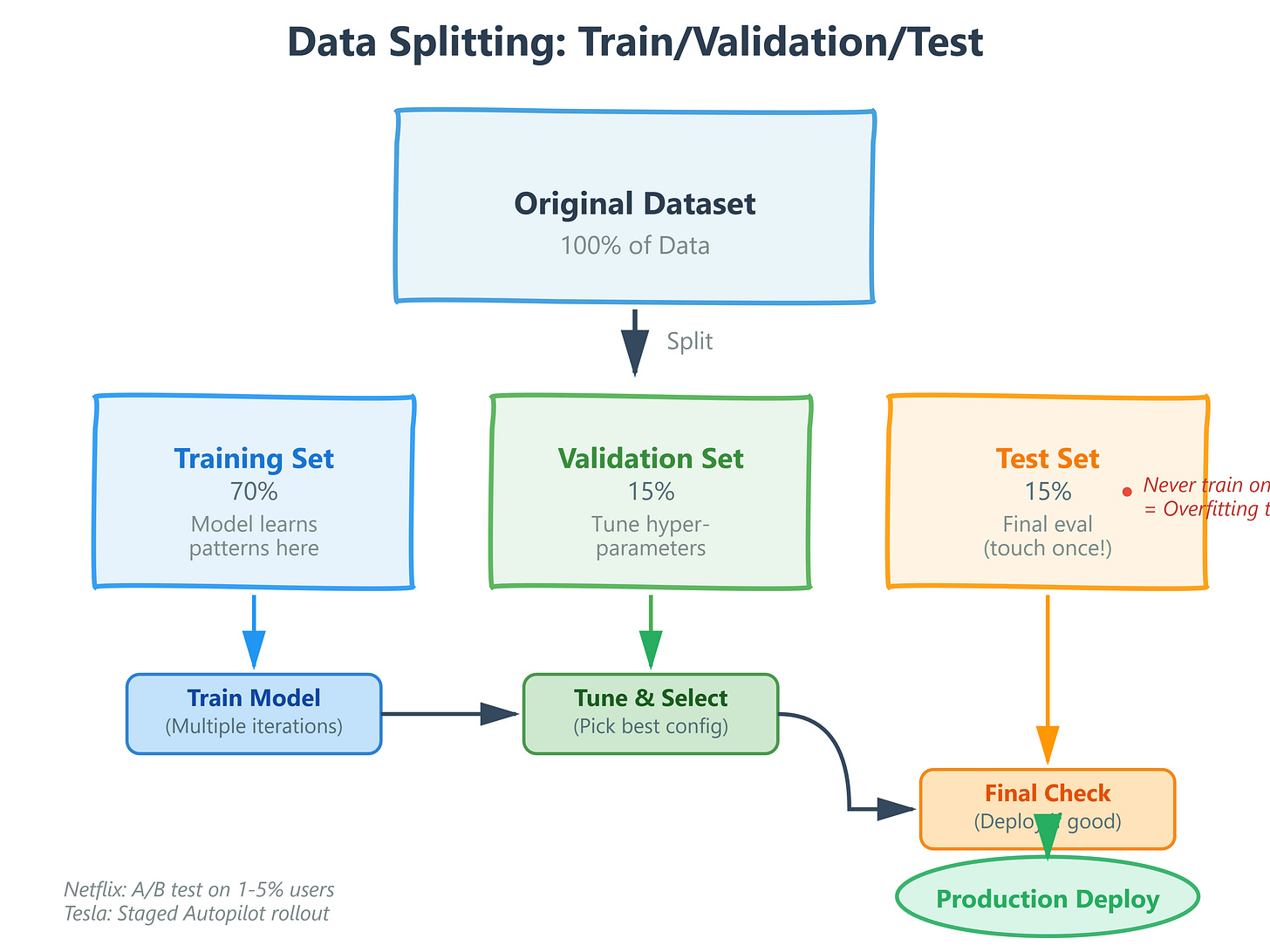
Core Concept: Three Safety Nets for Production AI
The Training Set (60-80% of data)
Your model learns patterns here. Think of this as the practice problems where you’re allowed to see the answers. At Spotify, when training their playlist recommendation system, they use 70% of user listening history to learn patterns like “users who like indie rock often skip pop country songs.”
Critical Insight: Training data size directly impacts model capacity. Too little data and your model can’t learn complex patterns. GPT-4 used trillions of tokens; your first models might use thousands. Both need proper splitting.
The Validation Set (10-20% of data)
This is your tuning dataset. You test different hyperparameters (learning rate, model architecture) and pick the best configuration. OpenAI trains multiple GPT model variants simultaneously, validates performance on held-out data, then selects the best architecture.
Production Pattern: At Google, every search ranking algorithm change is validated on 1% of traffic before wider rollout. They measure click-through rates, time-to-click, and user satisfaction on this validation set to predict full-rollout performance.
The Test Set (10-20% of data)
The final exam. You touch this data ONCE at the very end to verify your model generalizes. If you peek at test set performance during development and adjust your model, you’ve contaminated it – it’s no longer a true measure of real-world performance.
Real Failure Story: A major tech company (unnamed) built a fraud detection model showing 95% accuracy. They validated repeatedly on the same test set, tweaking until metrics looked perfect. In production, accuracy dropped to 67% because they’d effectively overfit to their test set. Cost: $12M in missed fraud in the first month.